INTRODUCTION
In a historic moment that has stirred immense national pride, India’s Air Force has officially claimed the title of the third most powerful air force in the world, surpassing China according to the World Directory of Modern Military Aircraft (WDMMA). This achievement isn’t just a number on a chart; it is something far more meaningful. It reflects India’s relentless pursuit of technological excellence, operational strength, and strategic modernization.
For readers who want a deeper understanding of India’s military evolution, this detailed book on IAF history offers rich insights into its missions, aircraft, and strategic milestones.
For a country that once relied heavily on imports and legacy aircraft, rising to the global top three marks a defining moment in its defense evolution.
WHAT DOES THIS RANKING MEAN?

Being listed alongside the United States and Russia signifies a major milestone in India’s defense journey. The Indian Air Force’s rise to the third spot represents strength, readiness, modernization, and capability.
This ranking showcases the IAF’s evolution from a regional air arm to a globally respected power capable of handling modern warfare, humanitarian operations, and strategic defense with precision.
It also strengthens India’s diplomatic and strategic position, opening doors for international collaborations, defense partnerships, and joint training programs. The world now sees India as a nation not only capable of safeguarding its own skies but also contributing meaningfully to global security frameworks.
Furthermore, the achievement reflects India’s success in defense self-reliance through initiatives like “Make in India”, which strengthens domestic technological independence.
The WDMMA list states:
USAF TruVal Rating (TVR): 242.9
Russia: 114.2
India: 69.4
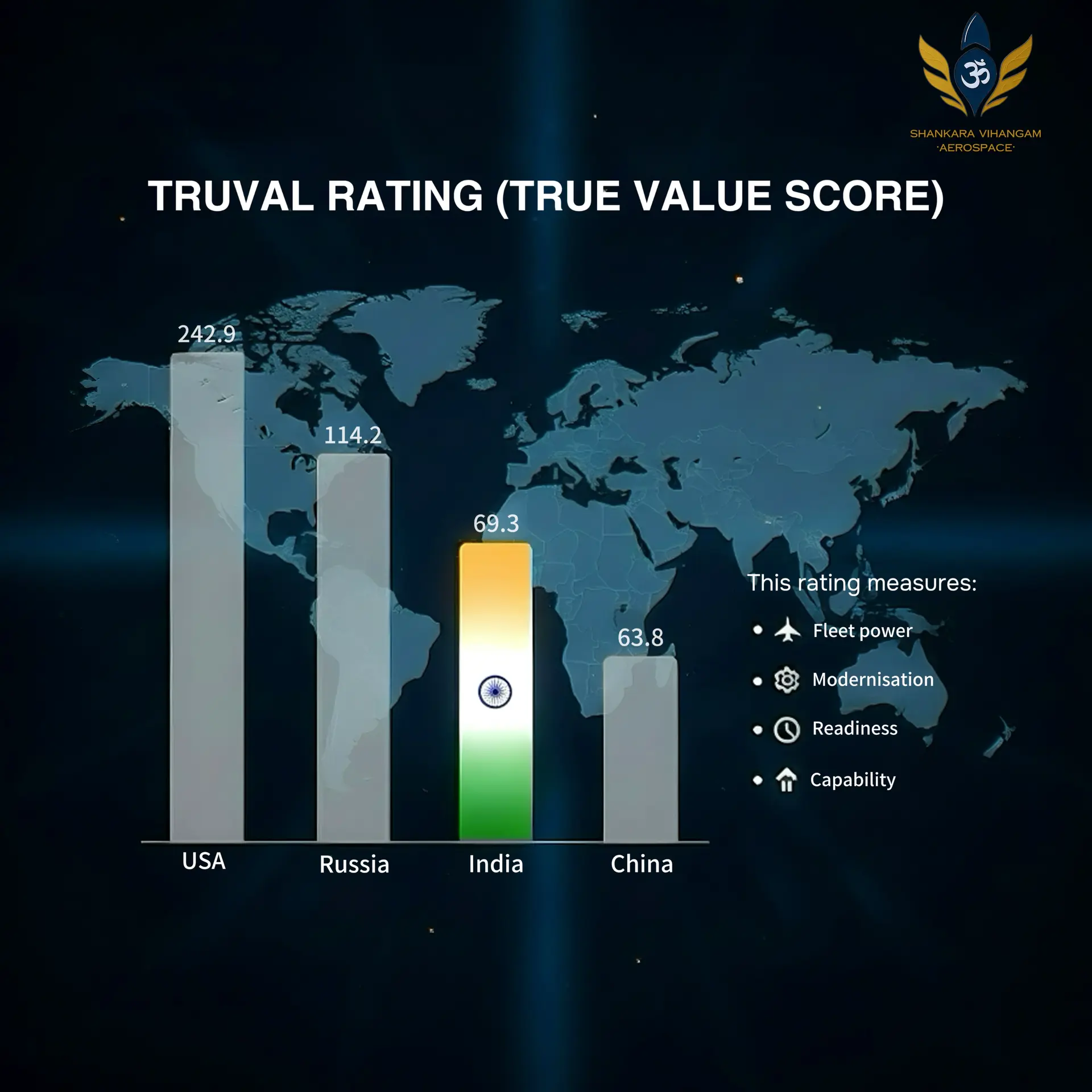
Following the top three are China (63.8), Japan (58.1), Israel (56.3), France (55.3), and the UK (55.3).
WHAT IS THE TRUVAL RATING?
The TruVal Rating (TVR), short for “True Value Rating,” is a scoring system developed by WDMMA to measure and compare the overall strength and effectiveness of a country’s air force.
In simple terms, it’s not just about how many aircraft a nation has — it’s about how capable, modern, and mission-ready they actually are.
TVR considers factors such as:
Fleet Strength: Total aircraft in service — fighters, bombers, transports, helicopters, and support aircraft.
Fleet Modernization: Upgrades, new inductions, and technological improvements.
Training and Readiness: Pilot skill levels, combat preparedness, and mobilization speed.
Maintenance and Logistics: Availability of spare parts, technician efficiency, and repair capabilities.
Mission Diversity: Ability to perform different mission types — air defense, strike, transport, surveillance, etc.
Force Balance: Maintaining the right mix of aircraft for maximum effectiveness.
India’s TVR of 69.4 reflects tremendous progress across modernization, training, logistics, and balanced force structure.
FLEET MODERNIZATION
Fleet modernization refers to upgrading or replacing old aircraft with newer, more advanced ones. Just like phones or computers become outdated, fighter jets and helicopters also need to be upgraded regularly.
A modern fleet means better safety, higher combat strength, and faster response capability.

Indian Air Force & Modernization Efforts
Recent Developments Include:
Induction of Advanced Fighters: Rafale and the indigenous Tejas join the fleet, boosting combat capability.
Upgrades to Existing Aircraft: Modernization of Su-30MKI with enhanced weapons and avionics.
New Helicopters: Apache and Chinook for attack missions and heavy-lift operations.
Advanced Surveillance Systems: Deployment of new drones and radar technology for better situational awareness.
Stronger Air Defense: Enhanced systems for faster threat detection and neutralization.
Enthusiasts can explore fighter jet technology at home with high-quality model aircraft and flight simulators, providing a hands-on way to understand aerodynamics, combat systems, and jet operations.
Future Plans
India aims to strengthen further with:
AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft): India’s upcoming stealth fighter.
Tejas Mk-2: More capable than the current variants.
Increased Squadron Strength: Expanding operational capabilities.
Technology Transfer & Global Collaborations: Partnering internationally to advance aerospace tech.
These advancements will help India maintain a future-proof, world-class air force.

PILOT TRAINING AND READINESS
Strength in the skies isn’t just about powerful jets — it’s about the people who fly them.
IAF pilots undergo some of the most rigorous training in the world. The IAF doesn’t just train pilots; it shapes sky warriors.
Training includes:
Basics on Hawk and Pilatus aircraft — mastering navigation, speed, and precision.
Virtual Simulation & VR Training — practicing high-risk missions safely.
International Exercises — flying with the world’s strongest air forces in real-world combat simulations.
These missions make IAF pilots battle-tested in peacetime, ready for any challenge.
Aspiring pilots or aviation enthusiasts can practice virtually with flight simulators or aviation courses, gaining hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of aerial maneuvers and mission planning.
LOGISTICS AND MAINTENANCE
The Logistics and Maintenance division ensures the IAF never runs out of what it needs — spare parts, fuel, weapons, tools, technicians, and support systems.
How the IAF Maintains Its Fleet
Daily inspections before and after every flight.
Pre-flight and post-flight checks to identify hidden issues.
Deep overhauls of engines, avionics, and airframes.
Lifespan extension programs for older aircraft.
The Technical Workforce
The backbone of maintenance is handled by Aeronautical Engineering Branch officers:
AE (Mechanical) — engines, hydraulics, fuel systems, airframes.
AE (Electronics) — avionics, sensors, radars, communication, and EW systems.
Use of Modern Technology
The IAF uses advanced systems for:
Predictive maintenance
Real-time engine monitoring
Digital spare parts tracking
Interconnected inventory across all air bases
This ensures seamless operations and prevents downtime.

FORCE BALANCE
Force balance refers to having the right mix of aircraft, personnel, infrastructure, and technology.

What IAF Balances
Aircraft Mix
Fighters, transports, helicopters, and surveillance aircraft.
Well-Trained Personnel
Enough pilots, technicians, and command staff for operational efficiency.
Infrastructure
Strategically located air bases, robust runways, hangars, and depots.
Future-Proofing
Investments in AMCA, drones, loyal wingmen, hypersonic tech, and advanced EW systems.
This holistic balance makes the IAF combat-efficient today and future-ready for tomorrow.
CONCLUSION
This achievement is more than a boost to national pride — it reflects years of discipline, investment, and evolution since the IAF’s establishment in 1932.
Being ranked alongside the United States and Russia is not a coincidence. It is the result of consistent modernization, operational excellence, and an unwavering commitment to national security.
Fleet modernization, pilot readiness, logistics, and balanced force structure all play critical roles in achieving this milestone.
For those fascinated by the Indian Air Force’s rise, consider exploring detailed IAF history books or experiencing fighter jets virtually through flight simulators and aviation kits. These resources provide both knowledge and hands-on exploration, helping enthusiasts and students appreciate the scale, technology, and skill behind India’s air power.
This ranking is a victory, but also a responsibility — a reminder that India’s air power is rising, maturing, and preparing for even greater heights.
As India continues to soar globally, this honor belongs to the countless men and women in uniform whose dedication ensures that the Indian Air Force truly touches the sky with glory.
AUTHOR BIO
👤 Author — Maitri Dubey
Maitri Dubey is an aviation writer and researcher at SVM Aero, focusing on delivering accurate, well-researched, and student-friendly content on aerospace technology, military aviation, and global air power.
REVIEWED BY
🛩️ Reviewed by — VSK Aditya Devisetty (Team SVM Aero)
With a passion for aerospace and aviation, VSK Aditya Devisetty ensures every article is accurate, reliable, and insightful for readers.
SOURCES & REFERENCES
World Directory of Modern Military Aircraft (WDMMA) — Global air force rankings & TruVal Rating
Indian Air Force — Official Website — Training, modernization, fleet info
DRDO — Indigenous systems, upgrades, R&D
HAL (Hindustan Aeronautics Limited) — Tejas, AMCA, helicopter programs
